Approach of NIKISA Hospital for patients recovering from Uncontrolled Diabetes:
The approach followed by NIKISA Geriatric Centre & Recovery hospital to help patients to recover from Uncontrolled diabetes is based on its experience over the last 9 years. NIKISA takes a holistic view in helping the patient to recover from Uncontrolled Diabetes. NIKISA employs Allopathic way of practice for management of uncontrolled diabetes. Persons with uncontrolled diabetes are referred to NIKISA hospital by the diabetologists. NIKISA has its own laboratory, equipment and professionals to deal with uncontrolled diabetes. The 6 steps followed at NIKISA Geriatric Centre & Recovery hospital are given below;
- Closely monitor the blood sugar to study and record the impact of current diet, exercise and medication practices being followed by the patient on blood sugar.
- Preparing plan of care on the basis of findings of 1 and 2 above.
- Ensuring taking of medicine, diet and practicing of exercises as per prescription.
- Health education and counselling to the patient.
- Providing a follow up time table to the patient.
Step 1: Monitoring of Blood sugar:
Glucose meters are a great tool, but sometimes you need to keep a closer eye on your blood sugar levels. A continuous glucose monitoring system, or CGM for short, is a compact medical system that continuously monitors your blood sugar levels in more or less real time (there’s normally a five-minute interval between readings).
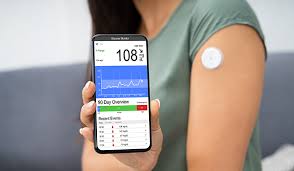
To use a CGM, a small sensor is pinned into the skin. An adhesive patch holds the sensor in place, allowing it to take glucose readings in interstitial fluid (the fluid that surrounds cells in the body) throughout the day and night. Generally, the sensors have to be replaced every 10 to 14 days.
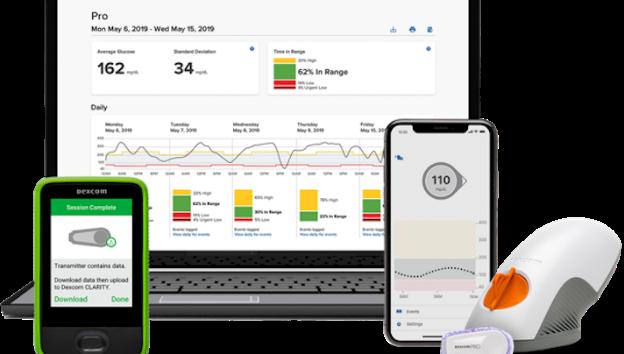
A small, reusable transmitter connected to the sensor allows the system to send real-time readings wirelessly to a monitor device that displays blood glucose data. The system tracks blood sugar levels day and night. It collects readings automatically every 5 to 15 minutes. It can help detect trends and patterns that give information to doctor so that a more complete picture of your diabetes is available for deciding the course of action. The data can help you find ways to better manage your condition.
Why Use CGM? Unlike traditional glucose meters, CGM records your blood sugar levels throughout the entire day and night, showing your highs and lows throughout the whole week. The systems can help:
- Record dangerously low overnight blood sugar levels, which often go undetected
- Track high levels between meals
- Show early morning spikes in blood sugar
- Evaluate how the present diet and exercise regime is affecting you
- Determine if your present treatment course is working on a day-to-day basis
What do we do with data obtained using CGM? We download data on your computer, tablet, or smartphone to see patterns and trends in your sugar levels. The information can help the diabetologist and nutritionist to make the best plan for managing your diabetes, including:
- How much insulin you should take?
- An exercise plan that’s right for you
- The number of meals and snacks you need each day
- The correct types and doses of medications
In acute cases when we use an insulin pump, we can also link it to the CGM system for continuous care. You won’t need to manually program the pump as with the other finger-prick methods. This is called a “sensor-augmented pump.”
Step 2: Stock taking of damage the body has already suffered on account of Diabetes: The following tests are conducted immediately on admission at the Geriatric Centre:
- Recording of vitals like height, weight, Sp o2, BP, Pulkse etc.
- Recording of infections in the body
- Blood tests:
- RBS
- Hb A1 c
- Lipid Profile
- Liver function tests
- Kidney function tests
- Electrolyte tests
- CBC
- Urine routine
- ECG
- Hearing test,
- Podiatry tests for detection of Diabetic neuropathy of the foot.
- Eye test to check for vision and fundus.
- Walking ability test:.
- To check impact on Pulse
- BP
- Spo2
- Recording of dietary habits and Diet being followed;
- Examination by a physician
- Examination by the diabetologist.
Step 3: Preparing Plan of Care: The Diabetologist, Dietician, Physician prepare a plan of care which would address the following issues:
- Prescription and medication regimen
- Diet prescription
Step 4: Taking measures to bring down the blood sugar and treatment of possible infections
- skin infections, such as cellulitis or ulcers, especially on the feet
- urinary tract infections, including cystitis
- mouth and gastrointestinal infections
- respiratory tract infections, such as tuberculosis (TB) and flu
- yeast infections, for example thrush
- ear infections
Step 5: Counselling to the patient
- Physician
- Diabetologist
- Physiotherapist
- Nutritionist
Step 6: Discharge and follow up plan
- Explaining of prescription along with Discharge instructions
- Providing a follow up schedule
Duration of Treatment Contemplated:
10 to 15 days.