Stroke rehabilitation
Approaches to stroke rehabilitation
There are many approaches to stroke rehabilitation. The rehabilitation plan will depend on the part of the body or type of ability affected by the stroke.
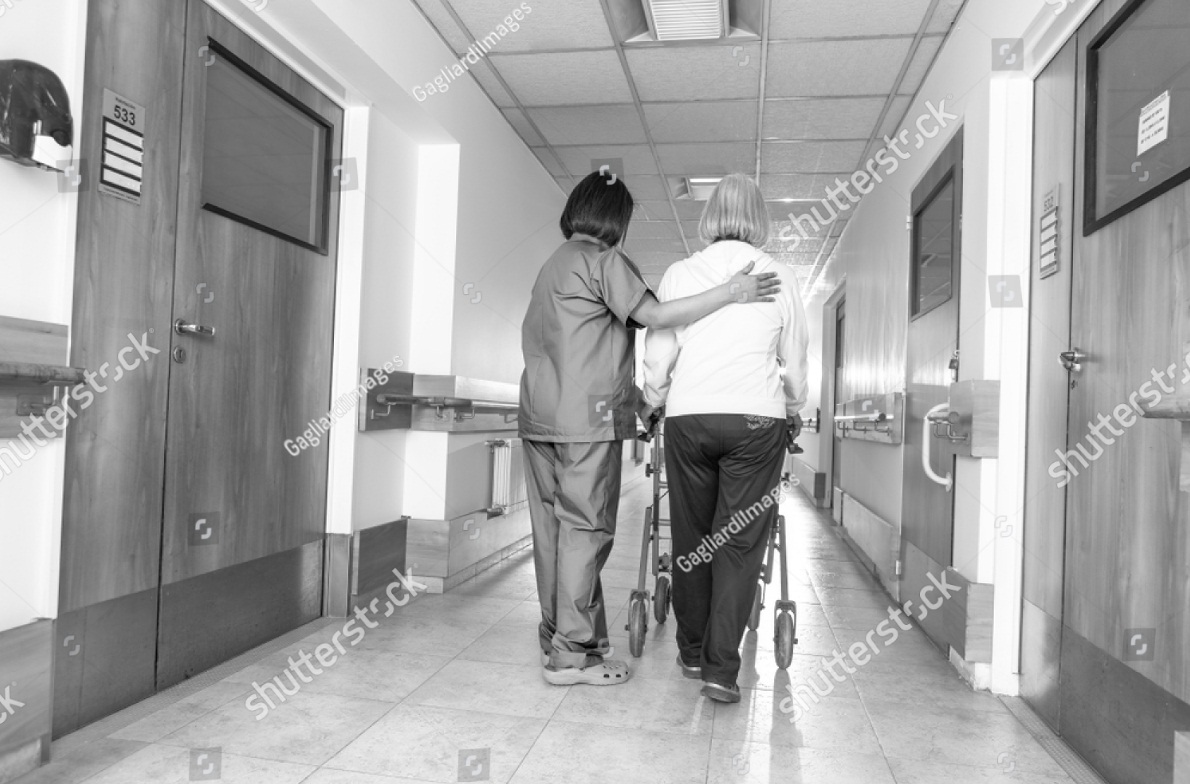

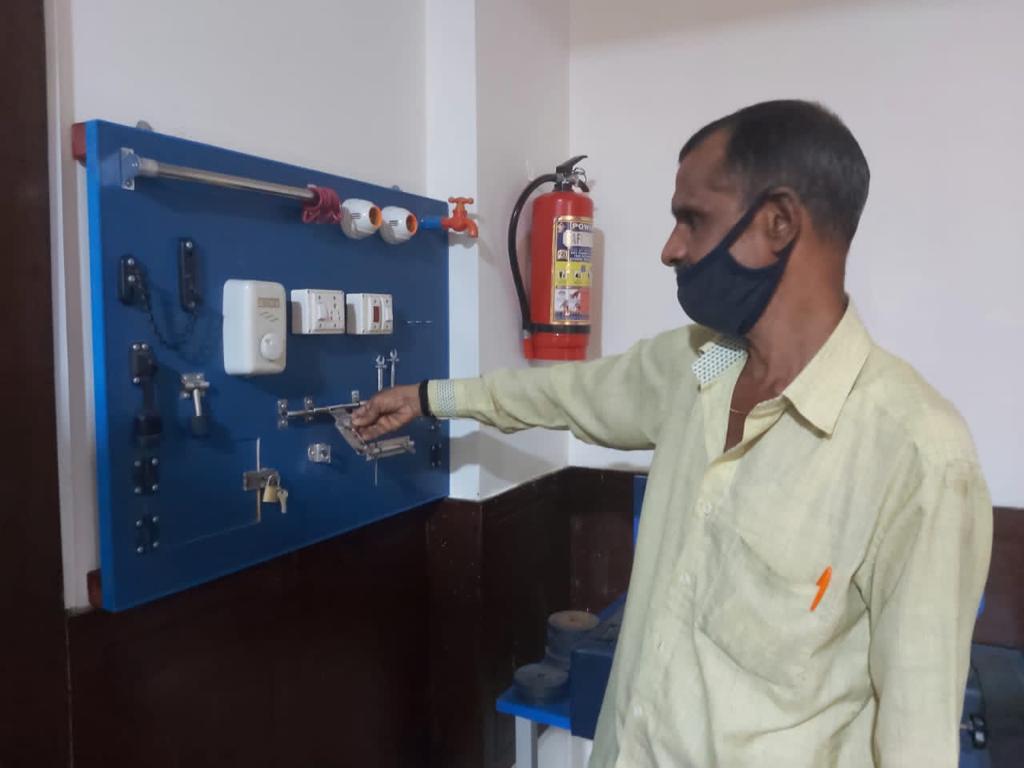
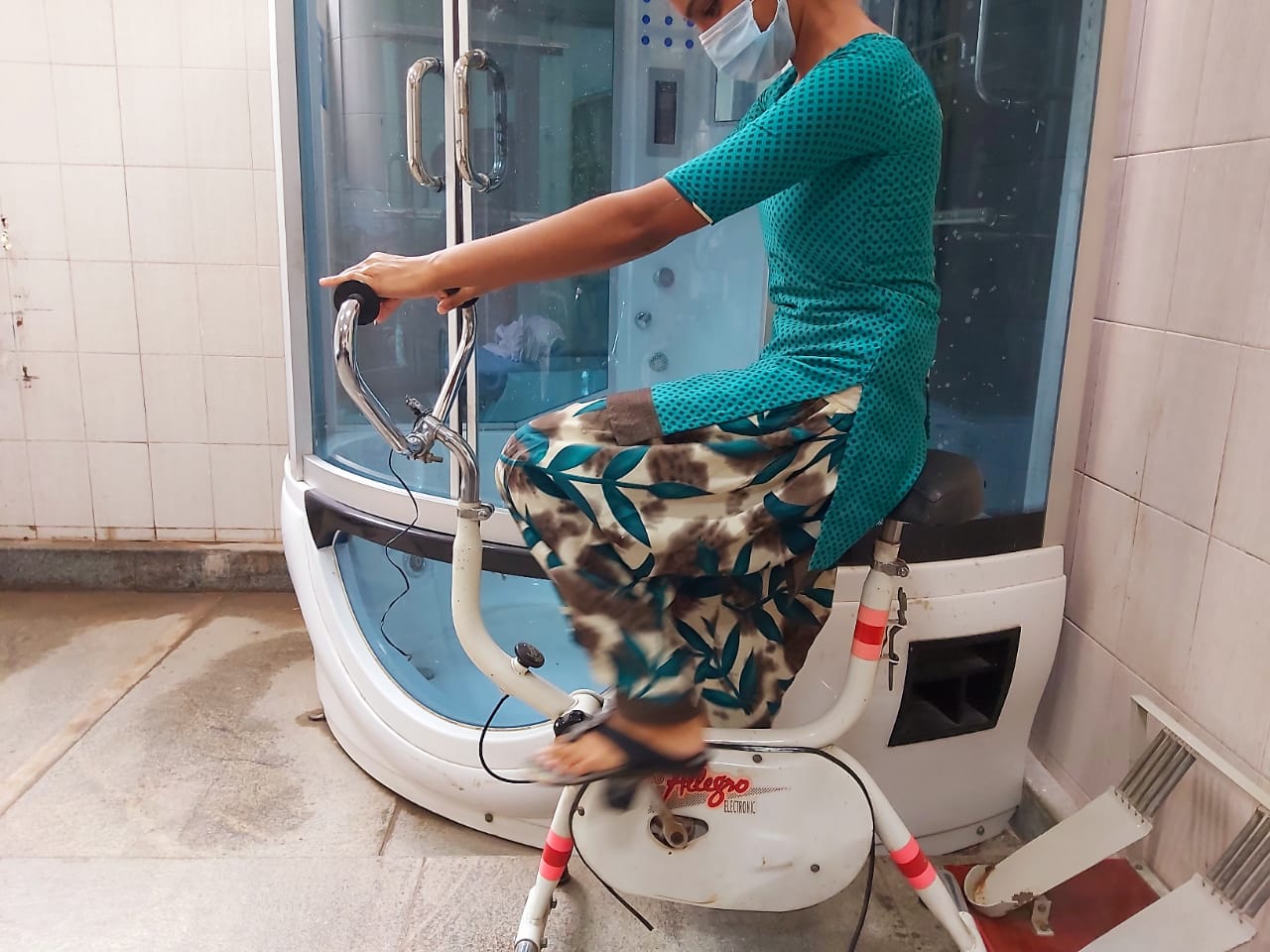
Physical activities for stroke recovering patients

Mobility training
Many stroke patients should be first trained to use mobility aids, such as a walker, canes, wheelchair or ankle brace. The ankle brace can stabilize and strengthen the ankle to help support body's weight while the patient relearns to walk.
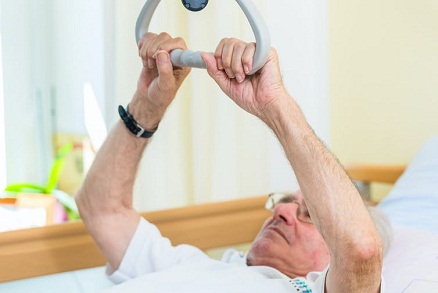
Range-of-motion therapy
Certain exercises and treatments can ease muscle tension (spasticity) and help the patient regain range of motion.
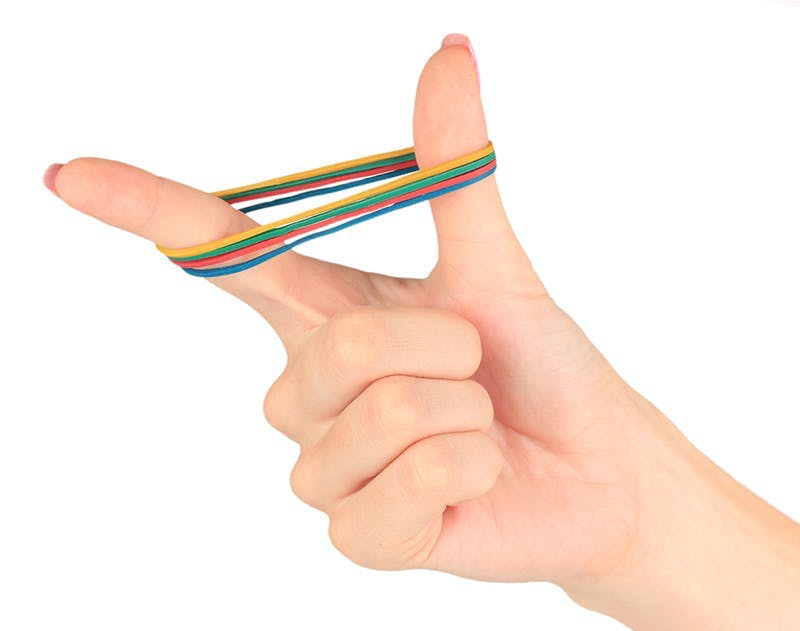
Motor-skill exercises
These exercises can help improve muscle strength and coordination. In most stroke patients, therapy is provided to strengthen swallowing.
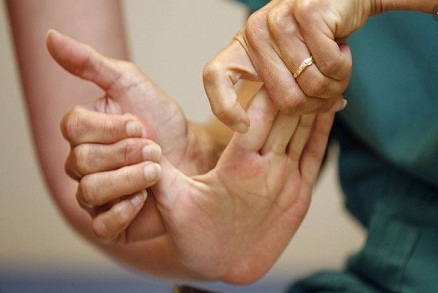
Constraint-induced therapy
This is basically aimed at rehabilitating the limbs. An unaffected limb is restrained while the patient practices moving the affected limb to help improve its function. This therapy is sometimes called forced-use therapy.
Technology-assisted physical activities
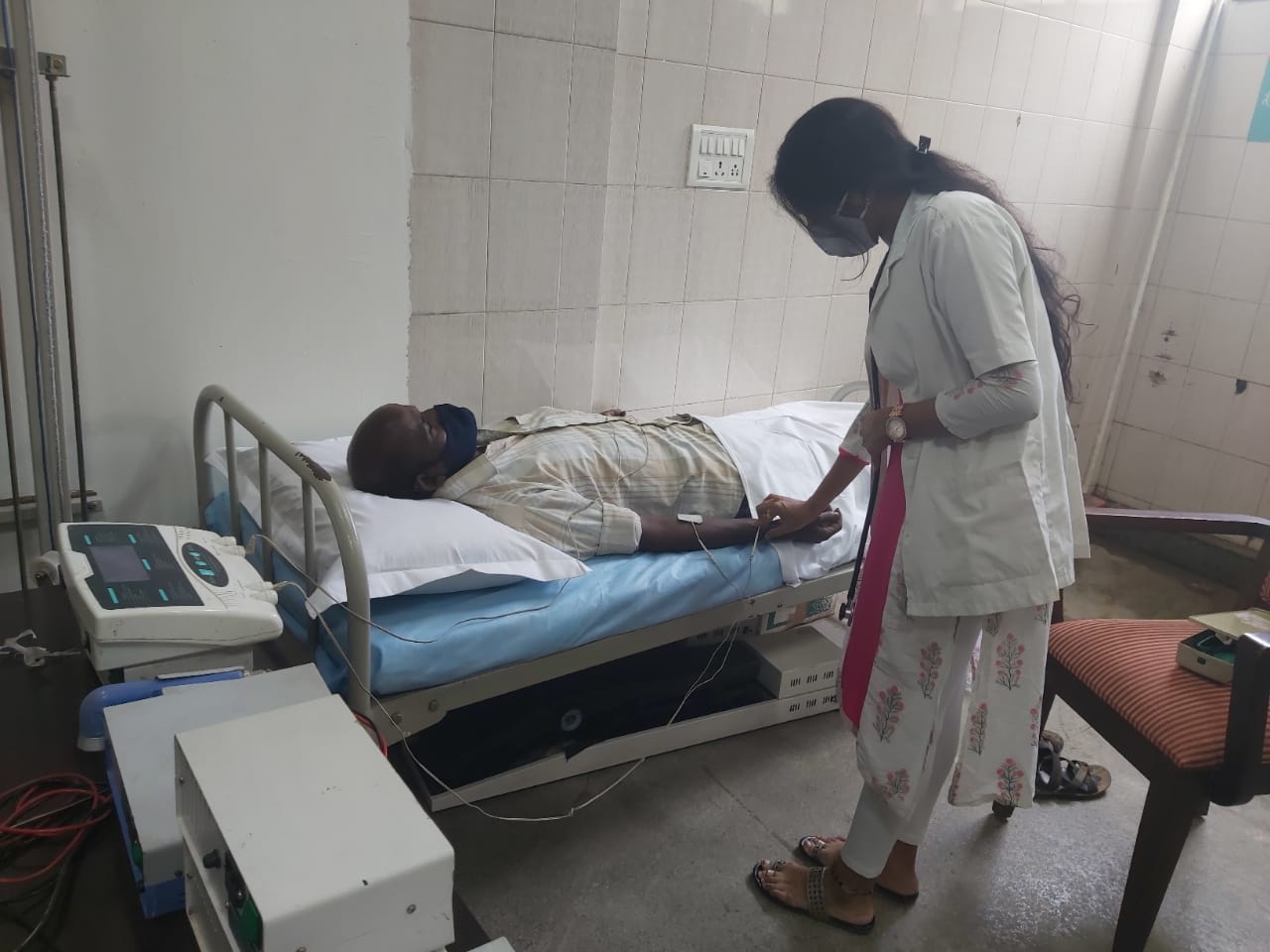

Functional electrical stimulation
Electricity is applied to weakened muscles, causing them to contract. The electrical stimulation may help re-educate patient’s muscles.

Machine assisted movements
There are machines which can assist impaired limbs with performing repetitive motions, helping the limbs to regain strength and function.

Virtual reality
The use of video games and other computer-based therapies involves interacting with a simulated, real-time environment.
Cognitive and emotional activities

Therapy for cognitive disorders
Occupational therapy and speech therapy can help to get back lost cognitive abilities, such as memory, processing, problem-solving, social skills, judgment and safety awareness.

Therapy for communication disorders
Speech therapy can help to regain lost abilities in speaking, listening, writing and comprehension.

Psychological evaluation and treatment
Emotional disturbance of stroke patients has to be addressed with proper counselling.
Medication and Diet
Proper nutrition and taking medication as per the prescription of nutritionist and the treating doctor respectively is of paramount importance in stroke recovery.
Most stroke patients get into a sedentary status, especially in-home settings and many develop secondary complications arising out of poor hygiene. Bed sores, urine and incontinence are very common in recovering stroke patients.
Usually Stroke patients suffer from disorders like diabetes and hypertension. It is very essential to monitor vital parameters.
Secondary Injuries: Unexpected fall is very common in stroke patients. When untrained personnel handle stroke patients some might suffer from limb and girdle fractures.

When should stroke rehabilitation begin?
The duration of stroke rehabilitation of a patient depends on the severity of the stroke and related complications. Some stroke survivors recover quickly. But most need some form of long-term stroke rehabilitation, lasting possibly months or years after their stroke. The sooner the stroke rehabilitation begins, it is more likely that the patient regains lost abilities and skills. Usually stroke rehabilitation should start as soon as 24 to 48 hours after the stroke and while the patient is at the hospital. However, the immediate priorities of the treating doctor at hospital are to:
- Stabilize the patient’s medical condition
- Control life-threatening conditions
- Prevent another stroke
- Limit any stroke-related complications
Because of the above reasons in many cases rehabilitation activities do not begin with in 24 to 48 hours.
What factors affect the outcome of stroke rehabilitation?
Stroke recovery varies from person to person. It’s hard to predict how many abilities the patient might recover and how soon. In general, successful stroke rehabilitation depends on:
- Physical factors, including the severity of stroke in terms of both cognitive and physical effects
- Emotional factors, such as patient’s motivation and mood, and patient’s ability to stick with rehabilitation activities outside of therapy sessions
- Social factors, such as the support of friends and family
- Therapeutic factors, including an early start to rehabilitation and the skill of the stroke rehabilitation team
- The rate of recovery is generally greatest in the weeks and months after a stroke. Earlier the recovery activities begin, faster would be the recovery. However, there is evidence that performance can improve even 12 to 18 months after a stroke.


Who participates in your stroke rehabilitation team?
Stroke rehabilitation involves a variety of specialists. Specialists who can help with physical needs include:
- Doctors: Physicians and Neurologists guide the recovery process and help prevent complications. They will help the patient to gain and maintain healthy lifestyle behaviours to avoid another stroke.
- Rehabilitation nurses:Our Nurses specialize in caring for people with limitations to activities can help the patient in incorporating the skills you learn into daily routine of the patient. Rehabilitation nurses can also offer options for managing bowel and bladder complications of a stroke.
- Physical therapists. These therapists help you relearn movements such as walking and keeping your balance.
- Occupational therapists. These therapists help you relearn hand and arm use for daily skills such as bathing, tying your shoes or buttoning your shirt. Occupational therapists can also address swallowing and cognitive issues, and safety in your home.
- Speech and language pathologists. These specialists help improve your language skills and ability to swallow. Speech and language pathologists can also work with you to develop tools to address memory, thinking and communication problems.
- Social workers. Social workers help connect you to financial resources, plan for new living arrangements if necessary and identify community resources.
- Psychologists. These specialists assess your thinking skills and help address your mental and emotional health concerns.
- Therapeutic recreation specialists. These specialists help you resume activities and roles you enjoyed before your stroke, including hobbies and community participation.
- Vocational counsellors. These specialists help you address return-to-work issues if that is a goal.
Where does stroke rehabilitation take place?
In good hospitals stroke rehabilitation begins while the patient is still at the hospital. But before being discharged from the hospital the patient’s family member should decide on the rehabilitation setting. The options include:
- Inpatient rehabilitation units. These facilities are either freestanding or part of a larger hospital or clinic. The recovering patients stay at the facility for up to two to eight weeks as part of an intensive rehabilitation program.
- Outpatient units. These facilities are often part of a hospital or clinic. They are utilised by recovering patients as “out Patient Services” usually for physiotherapy services. This is most common with Government hospitals.
- Old age homes. Old age homes are not specialised in rehabilitation activity. But some find it difficult to take care of patients at homes and they admit them to Old Age homes. Usually recovery aspect of a Stroke patient is not given the due importance in such places.
- Home-based programs. Providing home-based recovery services to stroke patients at home allows greater flexibility than other options. The major drawback is that the patient will not have access to specialized rehabilitation equipment and personnel. In addition, to provide services to stroke recovering patient one needs bed side attendant, physiotherapist etc. But many prefer this option and that is very often on account of lack of financial resources to support rehabilitation activities of the stroke patients.
